Understanding the USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement) shipping rules is crucial for small business owners and logistics managers aiming to thrive in today’s global market. The USMCA, signed on November 30, 2018, and replacing the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), modernizes and reshapes trade among the three North American countries. This transition, occurring right before the global COVID-19 pandemic, significantly changed how goods move across borders within North America.
Understanding these regulations can be challenging. From determining which products qualify for duty-free status to comprehending customs procedures, the details can often seem overwhelming.
But here’s some good news: shipping under the USMCA doesn’t have to be a bureaucratic nightmare. By mastering key provisions and understanding the required documentation, you can not only avoid common pitfalls but also significantly streamline your operations.
Table of Contents:
- Understanding USMCA Shipping Guidelines
- Rules of Origin Under USMCA
- Customs Procedures for USMCA Shipments
- Duty Deferral and Relief Programs
- Penalties and Seizures Related to USMCA
- Navigating USMCA Online Resources
- Industry-Specific Considerations
- Best Practices for Seamless USMCA Compliance
- FAQs in Relation to USMCA Shipping Guidelines
- Conclusion
Understanding USMCA Shipping Guidelines
The Agreement between the United States of America, Mexico, and Canada (USMCA) was a game-changer for trade between the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. It eliminated most tariffs and other barriers, making it significantly easier for companies to ship goods across borders.
Key provisions of USMCA related to shipping include eliminating tariffs, setting rules of origin to determine which goods qualify for preferential treatment, streamlining customs procedures, and establishing ways to resolve disputes. The goal was to boost economic activity between the three North American powerhouses.
To receive the USMCA benefits, shipments need a valid USMCA Certificate of Origin. This form proves the goods meet the USMCA rules of origin. Other documents like commercial invoices, bills of lading, packing lists, and any necessary permits or licenses are also required.
Overview of USMCA
The USMCA, signed into law in 2018 and effective in 2020, established the world’s largest free trade area. This agreement encompasses over 510 million people across the United States, Mexico, and Canada, representing nearly 30 percent of the global economy.
With a combined nominal GDP of $30.997 trillion, the USMCA significantly influences global trade dynamics. It aims to enhance trade relationships, boost economic growth, and create more balanced and equitable trade opportunities among the three nations, replacing NAFTA and addressing modern trade issues with updated provisions and regulations.
The agreement aims to:
- Eliminate trade barriers and facilitate cross-border movement of goods and services.
- Promote fair competition.
- Increase investment opportunities.
- Provide protection and enforcement of intellectual property rights.
- Create procedures for the resolution of trade disputes.
- Establish a framework for further trilateral, regional, and multilateral cooperation.
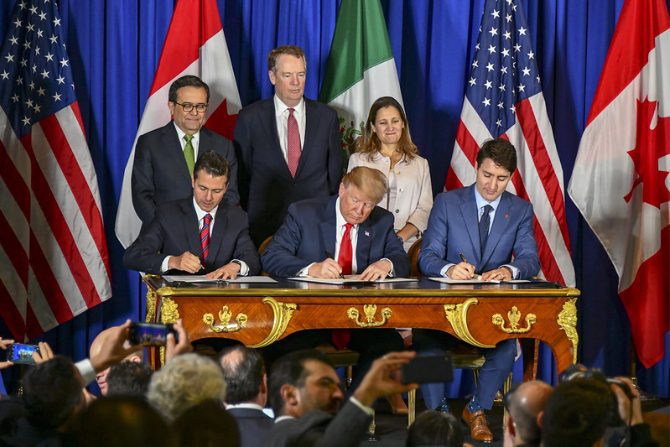

The leaders of the United States, Mexico, and Canada sign the USMCA on November 30, 2018, at the G20 summit in Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Key Provisions for Shipping
The USMCA has several provisions that directly impact shipping:
- Tariff Elimination: Most goods traded between the three countries immediately or phased out tariff elimination.
- Rules of Origin: These rules determine which goods qualify for USMCA tariff preferences.
- Customs Procedures: Streamlined procedures facilitate the movement of goods while ensuring compliance
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: These mechanisms address trade disagreements efficiently.
These provisions aim to make cross-border shipping easier, faster, and more cost-effective for businesses.
Required Documentation
To qualify for USMCA benefits, shipments must include:
- A valid USMCA Certificate of Origin, completed by the exporter.
- Commercial invoice.
- Bill of lading or airway bill.
- Packing list.
- Any applicable permits, licenses, or certificates (e.g., for restricted goods).
Accurate and complete documentation is critical to avoid delays, additional duties, or even seizure of goods by customs. Exporters need to ensure they understand the requirements and maintain detailed records.
Rules of Origin Under USMCA
USMCA’s rules of origin are the key to unlocking tariff benefits. They determine whether a product qualifies as “originating” in the USMCA region and can be shipped duty-free or at a reduced rate.
Determining Origin of Goods
A product can be considered USMCA-originating in several ways:
- Wholly obtained or produced entirely in the USMCA region (e.g., crops grown or animals raised).
- It is produced entirely in the USMCA region exclusively from originating materials.
- Produced in the USMCA region using non-originating materials but meeting specific rules of origin.
These specific rules can be complex. They are based on changes in tariff classification, regional value content, or sometimes both. Essentially, if a product uses any non-USMCA materials, it must be substantially transformed in a USMCA country to qualify.
USMCA Certificate of Origin
The USMCA Certificate of Origin is like the golden ticket for duty-free shipping. The exporter completes it, declaring that the product meets the USMCA rules of origin.
The certificate includes information such as:
- Exporter and producer details
- Description and HS tariff classification of the goods
- Preference criterion (how it qualifies as originating)
- Period of coverage (for multiple shipments of identical goods)
The importer relies on this certificate to claim USMCA tariff treatment at the border. Without the certificate, the importer cannot benefit from reduced duties.

Determining the origin of goods under USMCA involves ensuring products are either wholly obtained, produced entirely from originating materials, or substantially transformed using specific rules.
Origin Verification Process
Providing a USMCA certificate doesn’t guarantee that customs will accept it without verification. Customs officials have the right to verify the origin of the goods to ensure compliance.
This can involve:
- Sending written questionnaires to the exporter or producer
- Conducting visits to the exporter or producer’s facilities
- Requesting detailed records to support the origin claim
If the goods are found not to qualify, the importer may have to pay duties owed duties plus interest or even face penalties for false claims. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain accurate records and cooperate with any origin verification requests.
The bottom line is to know the rules, fill out the paperwork properly, and be ready to back it all up. That’s the key to smooth USMCA shipping.
Customs Procedures for USMCA Shipments
Managing customs can feel like trying to solve a Rubik’s cube blindfolded. But with some know-how (and perhaps a reliable customs broker), you’ll be managing USMCA shipments like a pro in no time.
Role of Customs Brokers
Customs broker act as your personal guides through the complexities of international trade. These licensed experts are well-versed in customs procedures, regulations, and documentation.
They can help you:
- Properly classify your goods and determine applicable duties
- Prepare and file customs entries and other required paperwork
- Pay duties and fees on your behalf
- Resolve issues with customs clearance
- Stay on top of changing regulations and requirements
While handling customs yourself is an option, brokers can save you time, headaches, and costly mistakes. They’re especially useful for complex shipments or if you’re new to the process.
Formal vs Informal Entry
Not all shipments are treated equally by customers. The type of entry required depends on the value and nature of the goods.
Formal Entries: Typically needed for commercial shipments valued at over USD 2,500. They involve more paperwork and scrutiny, including:
- Entry manifest or application
- Commercial invoice
- Packing list
- Bond (to ensure payment of duties)
- Other relevant documents (like the USMCA Certificate of Origin)
Informal Entries: For smaller or non-commercial shipments. The process is simpler, with fewer hoops to jump through.
Understanding these procedures and choosing the right type of entry can streamline your shipping process and ensure compliance with USMCA regulations.
Required Documentation
Regardless of the entry type, certain documents are essential for customs clearance under USMCA:
- USMCA Certificate of Origin (to claim preferential tariff treatment)
- A commercial invoice (with description, quantity, and value of goods)
- Packing list (itemizing contents of each package)
- Bill of lading or airway bill (contract of carriage with the carrier)
- Other relevant permits, licenses, or certificates (depending on the goods)
Pro Tip: Double-check that all your documents are complete, consistent, and legible. Customs agents prefer easy-to-read paperwork.
Clearing Customs
The final step is securing the release of your goods from customs and getting them on their way. For USMCA shipments, the process generally involves:
- Filing the entry and presenting the required documents.
- Paying any applicable duties, taxes, and fees.
- Undergoing examination or inspection (if selected by customs).
- Obtaining the release of the goods into the importing country’s commerce.
If your documentation is accurate and you comply with regulations, your goods should pass through customs smoothly. However, if issues arise, be prepared to provide additional information or face potential delays or penalties.
The key is to stay organized, communicative, and on top of the ever-changing world of customs When in doubt, don’t be afraid to call in reinforcements in the form of a trusty customs broker.

Clearing customs involves filing entries, paying duties, undergoing inspections, and ensuring proper documentation and compliance to avoid delays or penalties.
Duty Deferral and Relief Programs
Let’s face it: paying duties isn’t exactly thrilling. But what if there were ways to defer, reduce, or even eliminate those charges? Enter USMCA’s duty deferral and relief programs – your allies in managing cross-border shipping costs.
Overview of Programs
USMCA countries offer a range of programs to help alleviate the duty burden for qualified shipments. Some popular options include:
- Customs bonded warehouses (store goods duty-free until ready for sale)
- Temporary importation under bond (import goods temporarily without paying full duties)
- Duty drawback (get a refund on duties paid on imported materials that are later exported)
- Foreign trade zones (special areas where goods can be stored, processed, or manufactured duty-free)
These programs can be a game-changer for businesses looking to reduce costs and improve cash flow. But like most things in life, there’s a catch: each program has its own set of rules and requirements that must be meticulously followed.
Eligibility Requirements
So, how do you know if your goods qualify for one of these duty-saving programs? It all comes down to the essential details.
Factors to consider include:
- Type of goods (some programs have restrictions)
- Purpose of importation (e.g., storage, processing, re-export)
- Length of time goods will stay in the country
- Compliance with security and record-keeping requirements
For instance, to qualify for duty drawback, you’ll need to prove that the imported materials were actually used in the production of exported goods. You must post a bond for temporary importation and ensure the goods are re-exported within a specified timeframe.
Application Process
Ready to take the plunge and apply for a duty deferral or relief program? Now, it’s time to dive into the wonderful world of paperwork.
The application process typically involves:
- Determining which program is the best fit for your goods and business needs.
- Gathering required documentation (think: detailed product info, shipping records, proof of export).
- Filling out the appropriate application forms (each program has its own).
- Submitting the application package to the relevant customs authority.
- Undergoing a review process (customs will scrutinize your application to ensure eligibility).
- Receiving approval and setting up the necessary bonds or accounts.
The process may be complex, but the potential duty savings can be worthwhile. And if the thought of tackling it alone makes you break out in hives, remember that there are always customs brokers and trade attorneys who can help guide you through the process.
The bottom line? USMCA’s duty deferral and relief programs are a powerful tool in the savvy importer’s toolbox. With a bit ofknow-how and patience for paperwork, you, too, can unlock their money-saving potential. Happy shipping.
USMCA has simplified shipping between the U.S., Canada, and Mexico by eliminating tariffs and making it easier to move goods across borders. To benefit from these advantages, ensure your shipments include a USMCA Certificate of Origin and other essential documents. Understanding customs procedures and accurately completing paperwork is crucial for a smooth process.
Penalties and Seizures Related to USMCA
Violating USMCA rules can result in severe consequences, including penalties, seizures, and the loss of preferential tariff treatments. Here’s what you need to watch out for:
- False Claims: Misrepresenting the origin or characteristics of goods.
- Poor Record-Keeping: Failing to maintain accurate and complete records.
- NeglectingOriginVerifications: Ignoring requirements for verifying the origin of goods.
- Misclassification and Valuation Errors: Incorrectly classifying goods or misstating their value.
Penalties for violating USMCA rules are severe. In the U.S., importers involved in fraud, gross negligence, or even simple negligence can face civil penalties up to the value of the merchandise. Customs may also require payment of any duties that would have been due without USMCA benefits. In extreme cases, criminal penalties might apply. Mexico and Canada enforce similar penalty systems, ensuring strict compliance across all three countries.
Seizure Procedures
Penalties are one consequence, but customs authorities can also seize goods that violate USMCA rules. Here’s how the seizure process generally works:
- Detainment: Customs physically detain the goods.
- Seizure Notice: A notice is issued to the importer detailing the reasons for the seizure.
- Response Opportunity: The importer can address the issue, including providing additional documentation or resolving discrepancies.
In some cases, you may be able to secure the release of your goods under bond while resolving the issue.
If you believe the seizure is unjust, you can contest it through administrative or judicial procedures. Alternatively, you can abandon the goods, which means accepting a loss.
Handling a seizure is complex and challenging, so ensuring compliance with USMCA rules is crucial to avoid such situations.

USMCA violations can lead to penalties, seizures, and denial of preferential tariff treatments for false claims, poor record-keeping, and misclassification of goods.
Navigating USMCA Online Resources
With NAFTA replaced by the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), accessing the latest information online is crucial. Official sources include:
- The U.S. Trade Representative’s website
- Canada’s Global Affairs site
- Mexico’s Ministry of Economy portal.
Additionally, you can find updated guides and tools through trade organizations and industry-specific resources. Staying informed through these platforms will help you navigate the new trade landscape effectively and adapt to the changes brought by the USMCA.
Official Websites
When in doubt, always go straight to the source. The U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) has a reliable USMCA Center on its website, which provides extensive guidance on implementing the new agreement.
Canada and Mexico have also stepped up their online game. The Canada Border Services Agency has a CUSMA page (because they couldn’t call it USMCA like everyone else), and Mexico’s Tax Administration Service (SAT) has a T-MEC section on their site.
Guides and Manuals
If you prefer your information in a more detailed format, government agencies and trade organizations have got you covered with guides and manuals.
The CBP has put together a useful document USMCA Implementing Instructions that breaks down all the key changes. Industry groups like the American Association of Exporters and Importers (AAEI) also offer webinars and compliance manuals to help you clarify the new rules.
Helpful Tools
For those who like to be hands-on with their trade compliance, there are some efficient online tools to make their lives easier.
The CBP website has a fillable USMCA Certificate of Origin template that you can use to certify your goods. If you’re having trouble classifying your products, the FTA Tariff Tool is a searchable database that helps you quickly find your product’s tariff and rule of origin.
For those looking to further streamline their USMCA compliance, trade automation software is available, though it involves a more complex setup.
Industry-Specific Considerations
While USMCA brought changes for everyone, some industries felt the impact more than others. Here’s a quick rundown of how the new agreement affects key sectors.

USMCA brought significant changes to key industries, including stricter content requirements for autos, maintained yarn-forward rules for textiles, and expanded market access for agriculture.
Automotive
The auto industry experienced some of the significant changes under USMCA. To qualify for preferential treatment, passenger vehicles must have 75% North American content, up from 62.5% under USMCA.
The agreement also requires 70% of a vehicle’s steel and aluminum from North America and 40-45% of automotive content to be produced by workers earning at least $16 per hour. These changes aim to boost regional production and sourcing, presenting challenges for automakers.
Textiles and Apparel
USMCA maintained most of NAFTA’s “yarn-forward” rules of origin for textiles and apparel, meaning the yarn or fabric used to make the final product must come from a USMCA country.
However, the new agreement expanded the Tariff Preference Level (TPL) allowance for certain non-originating fabrics and made-up goods. It also introduced a chapter on textile and apparel customs enforcement and cooperation, highlighting the importance of this sector.
Agriculture
USMCA largely preserved and expanded market access for agricultural products. It retained zero tariffs on most agricultural goods while opening up the Canadian market a bit more for U.S. dairy, poultry, and eggs.
The agreement also includes chapters on sanitary and phytosanitary measures and agricultural biotechnology, addressing food safety and GMOs. If you’re in agriculture, it’s crucial to thoroughly review product-specific rules of origin and quotas under USMCA to ensure compliance. Understanding these regulations helps avoid penalties, manage tariff benefits, and ensure smooth market access. Staying informed about these details is key to effectively navigating the new trade landscape.
Best Practices for Seamless USMCA Compliance
So, you want to be a USMCA compliance superstar? It’s not as hard as you might think. With a little bit of organization and a lot of attention to detail, you can navigate through customs without breaking a sweat.
Record Keeping
The key to USMCA compliance is meticulous record-keeping. You should keep USMCA Certificates of Origin, supporting documents, and proof of origin for at least five years after importation.
Your records need to back up your USMCA claims and be easy to find in case of an origin verification or audit. Many companies use electronic record-keeping systems to store and retrieve USMCA documents efficiently. Because, let’s face it, no one wants to dig through a mountain of paperwork.
Internal Audits
Regular internal audits are a great way to catch USMCA compliance issues before they become penalties or enforcement actions. An effective USMCA audit program should review import and export transactions, record-keeping practices, origin determinations, and customs procedures.
Internal staff or external consultants with USMCA expertise can conduct the audits. Document your audit findings and corrective actions to show customs that you’re on top of your game.
Training and Education
To maintain USMCA compliance, ensure that your customs personnel, logistics staff, and all others involved in cross-border transactions are well-versed in USMCA rules, procedures, and documentation requirements.
Many professional organizations offer USMCA training, including the American Association of Exporters and Importers (AAEI) and the National Customs Brokers & Forwarders Association of America (NCBFAA). So, there’s no excuse for being uninformed.

For seamless USMCA compliance, maintain meticulous records, conduct regular internal audits, ensure staff are well-trained, and stay updated on rule changes.
Staying Current on Changes
USMCA rules and procedures can change over time, so it’s important to stayinformed. Customs authorities and trade organizations frequentlypost USMCA updates and guidance on their websites.
You can also subscribe to relevant email lists, attend industry events, and watch trade publications to stay current. And if all else fails, don’t be afraid to consult with customs brokers, trade attorneys, or other experts who can help you navigate the ever-changing world of USMCA compliance.
Don’t let USMCA violations catch you off guard. Avoid penalties and seizures by keeping accurate records, knowing your goods’ origins, and staying up-to-date with USMCA changes. Use official resources for guidance and consider automating compliance to make life easier.
FAQs in Relation to USMCA Shipping Guidelines
What is USMCA in shipping?
USMCA smooths out trade between the US, Canada, and Mexico by slashing tariffs and making cross-border shipping easier.
What are USMCA rules?
The rules outline who gets tariff cuts or none at all. They focus on where products were made and their materials’ origins.
What items qualify for USMCA?
To qualify, goods must meet specific origin criteria set by USMCA, proving they’re made in North America.
Is a USMCA certificate required?
Absolutely. It’s your golden ticket to claim benefits under the agreement but only if your goods tick all the right boxes.
Conclusion
So there you have it – diving into the world of USMCA shipping guidelines might initially feel like deciphering an ancient script written in legalese mixed with bureaucrats. However, once decoded, it is a manageable roadmap for more efficient and cost-effective cross-border trade practices.
In our journey through this guide’s ins and outs—from determining product eligibility under strict rules of origin criteria to mastering customs clearance processes—we’ve uncovered that while compliance requires attention to detail and patience during paperwork preparation, ultimately, it paves the way toward expanding your market reach without facing hefty tariffs or delays at border crossings.
The takeaway? Embrace these regulations rather than fear them. Knowledge of how exactly they work ensures smoother sailing ahead on international waters that once seemed perilously complicated.


